Ethanol Dehydration To Diethyl Ether

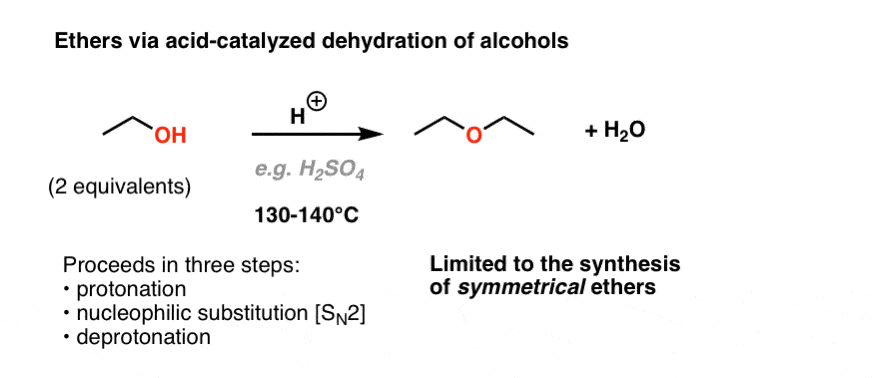
The dehydration of secondary and tertiary alcohols to get corresponding ethers is unsuccessful as alkenes are formed easily in these reactions.
Ethanol dehydration to diethyl ether. If ethanol is dehydrated to ethene in presence of sulfuric acid at 433 k but as 410 k ethoxyethane is the main product. The results shown the biggest surface area is 184 52 m2 gram at catalyst production at 10 hours for time dealumination. First alumina catalysts were catalytic dehydration of ethanol to ethylene and diethyl ether over alumina catalysts containing different phases with boron modification springerlink. Ethanol can be dehydrat ed through intramolecular route to produce ethylene or via intermolecular pathway to obtain diethyl ether dee 1.
The catalyst product then used for ethanol dehydration to produce diethyl ether. The effect of the presence of water on reaction performance was also evaluated. The catalytic ethanol dehydration of ethanol over the solvothermal derived alumina catalysts was investigated in this study. Metal loaded samples were prepared by wet impregnation and characterized using specific surface area measurements x ray diffraction and temperature programmed desorption of nh 3 the presence of fe on zsm 5 did not change the acidity of zsm 5 but did decrease its.
In situ chemical titration using pyridine as a titrant. Many studies have been investigated on the correlation between the catalyst properties and catalytic performances in ethanol dehydration. The catalytic ethanol dehydration. The reaction to make diethyl ether is reversible so eventually an equilibrium between reactants and products is achieved.
The steady state rates of ethene and diethyl ether formation in parallel ethanol dehydration reactions at 573 and 623 k are mechanistically and kinetically described by the same rate expression on different alumina materials α γ and η al 2 o 3 implying that alumina materials have similar surface sites under reaction environments. No significant negative impact of water over diethyl ether. Getting a good yield of ether which in turn requires that ether is distilled out of the reaction mixture before it reverts to ethanol. In the present work mechanistic pathways and kinetics of catalytic dehydration of ethanol were investigated in a closed batch reactor for the formation of diethyl ether and ethylene over the synthesized nio loaded hzsm 5 in the range of 160 240 c.