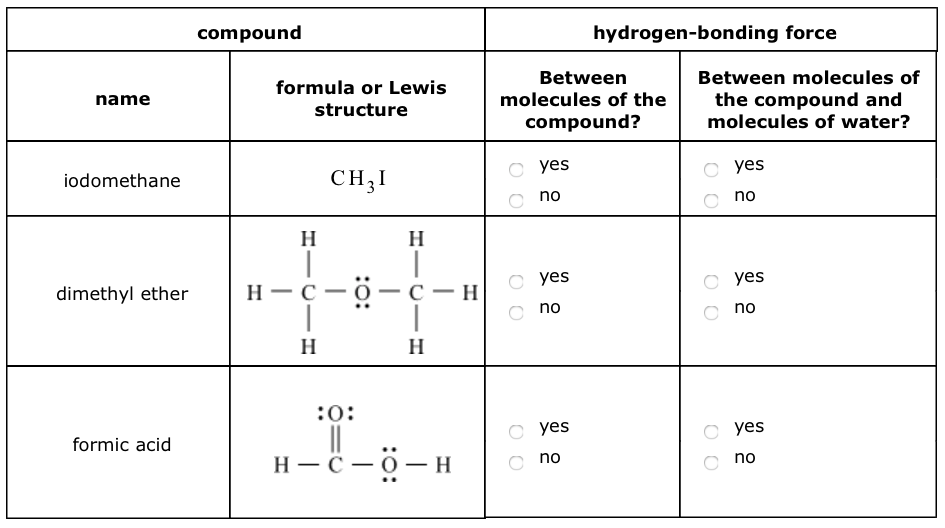
Dimethyl Ether Hydrogen Bonding

A hydrogen attached to carbon can also participate in hydrogen bonding when the carbon atom is bound to electronegative atoms as is the case in chloroform chcl 3.
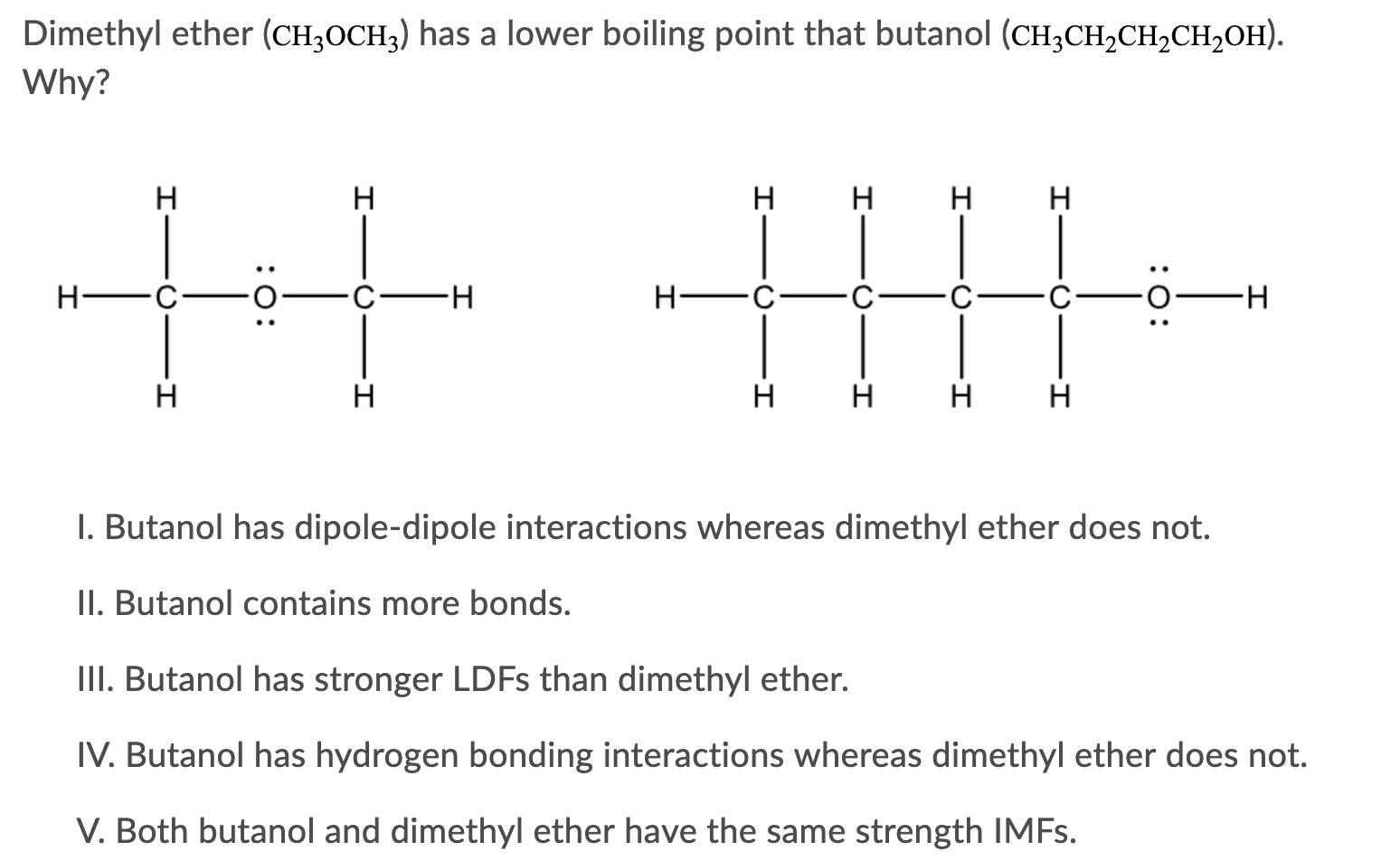
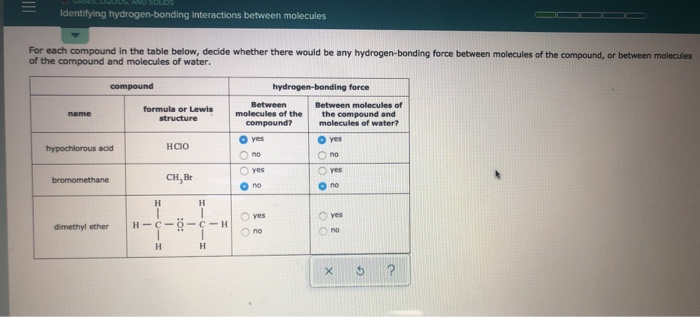
Dimethyl ether hydrogen bonding. C dimethyl ether forms hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds have about a tenth of the strength of an average covalent bond and are being constantly. Ethyl methyl ether three carbon atoms one oxygen atom is more soluble in water than 1 butanol four carbon atoms one oxygen atom even though both can engage in hydrogen bonding with water. D dimethyl ether has dispersion intermolecular forces.
So in pure dimethyl ether hydrogen bond does not occur. Can dimethyl ether hydrogen bond. Ethers are known to be mainly unreactive good. A dimethyl ether is polar.
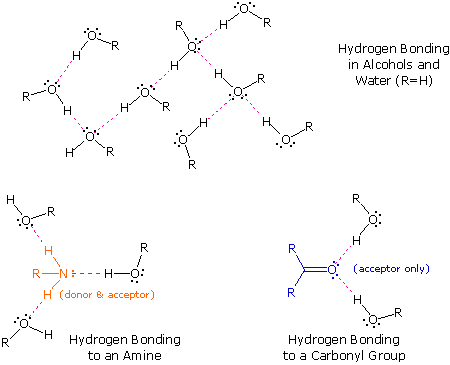
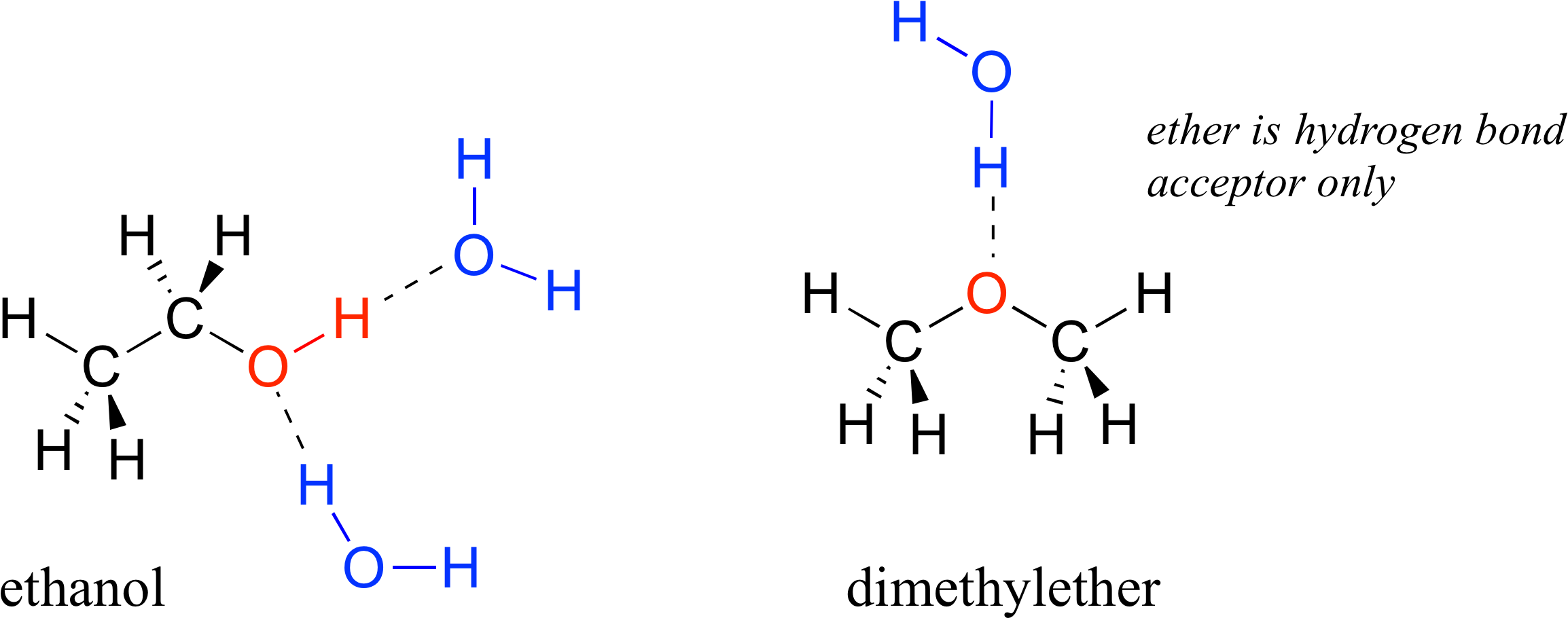
The structure of the dimethyl ether is as follows. F ethanol is polar. E dimethyl ether has ionic intramolecular attractions. Diethyl ether contains an oxygen atom that is a hydrogen bond acceptor because it is not bonded to a hydrogen atom and so is slightly negative.
Hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular force that is it occurs between molecules and is specific to hydrogen and either fluorine oxygen or nitrogen. A carrier for a hair care product containing polyvinylpyrrolidone was prepared with 77 04 g 70 aq dimethyl ether 14 11 g dimethyl ether 1 09 g co2. Here no hydrogen atom is attached to oxygen atom. Diethyl ether has no intermolecular hydrogen bonding because there is no oh group.
G ethanol has dispersion intermolecular forces. An aerosol mixt contains dimethyl ether 28 97 38 5. H ethanol is a carboxylic acid. The molecular formula of diethyl.
An attractive intermolecular force between hydrogen atoms bonded to an electronegative atom oxygen o nitrogen n or fluorine f atom and an unshared electron pair on nearby electronegative atom. Dimethyl ether ch eq 3 eq och eq 3 eq is a type of organic compound.